The Complete Guide to Corporate Records Management

Corporate records management may not strike you as an urgent and cutting-edge challenge for business thought leaders around the globe. However, one statistic might change your mind: Data creation in human activities has grown more than 1,200% in the last ten years – up from 6.5 zettabytes in 2012 to 79 zettabytes in 2021 – and will double again before 2025.
This means that your business almost certainly generates more information today than ever before – in emails, documents, social media interactions, and everything that passes into your website’s databases.
Much of this information should be persisted in your corporate records – although a good portion of it cannot or should not be. How businesses manage the inflow and retention of information into their records has consequences for long-term profitability and viability in the era of digital transformation.
Let’s look into how you can integrate corporate records management into your plan for this year.
Key Takeaways:
- Records should have a clearly defined lifecycle within any corporate organization.
- Two factors determine the most important records management priorities for any business. These are potential legal obligations and the estimated cost of inefficient or insufficient records-keeping practices.
- While most businesses still rely on a combination of paper and digital processes, the future of records management is digital and automated.
What is Records Management?
Records management is a specialized kind of document management focused on the intake and preservation of vital information within an organization.
READ ALSO:
10 Best Document Management Software for Small Businesses in 2024
10 Best Document Scanning Software for Windows 10 Users in 2024
Businesses create all kinds of documents – invoices, receipts, communications such as emails and texts, marketing materials, estimates, contracts, among a host of others. Wherever these documents record business operations in action, you have a record.
Most records simply preserve the information organizations need to carry out their operations. Others preserve potential legal evidence and are kept for the sake of compliance and liability protection. Records management is the application of a system to determine what becomes a record in an organization and how those records are preserved, accessed, and – in some cases – destroyed.
4 Stages of the Records Management Lifecycle
Digitally or on paper, you simply cannot store all the records your business operations inevitably create – nor should you. From financial transactions to medical records, much of the information that flows into business databases can quickly become a liability if improperly handled.
Regardless of the industry, your business almost certainly has records scattered across an uncharted landscape of paper documents, emails, and electronic files stored in different systems. Records management can help navigate this landscape.
To help you effectively manage records, each record should go through a lifecycle consisting of four stages that determine how records are handled within an organization.
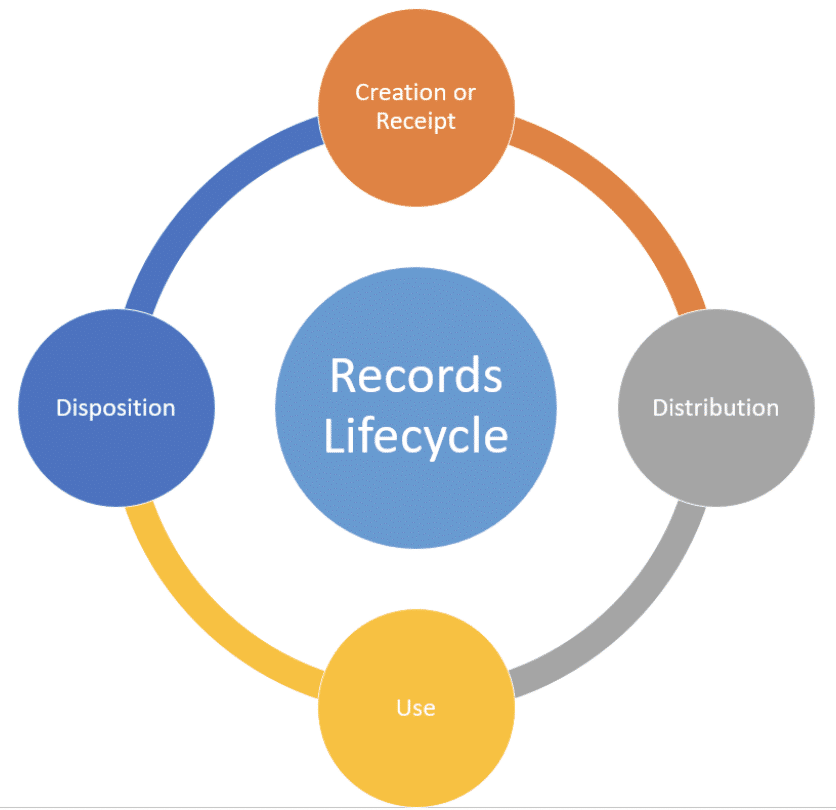
1. Creation
Rules for record creation should clearly define which documents become official records. Whether or not a document records business operations is the primary determining factor.
2. Distribution
In the distribution stage, organizations classify records for storage and retrieval. Records classifications may determine the repository where records are stored and who has access to them.
3. Use
Regardless of their different classifications, all records exist in a system to be retrieved at some point in the performance of business operations. As long as a record potentially affects current operations, it remains in use and should be easily located according to defined search criteria.
4. Disposition
Many types of records eventually cease to have any potential value for current operations. Others, such as patient records or customer card information in guest transactions, contain information that companies are only permitted to possess for limited periods.
Disposition divides records into permanent and temporary. Organizations keep permanent records indefinitely but may not prioritize their retrieval. All temporary records should have scheduled deletions.
What Should You Prioritize When Managing Records?
Sound record management in any business begins with a clear understanding of what kinds of records you could be obligated to produce and how quickly you can do so under time constraints.
1. Keep Audit-Ready Records
Beyond payroll and financial statements, the kinds of records auditors may require vary widely across retail, healthcare, law, or food and beverage industries. Nevertheless, audit preparedness will always involve establishing a few key priorities.
- Stay Current on the Law: Know what federal and state compliance regulations apply to the professional licenses and certifications you require to operate.
- Establish Version Control: Define the rules for creating paper and digital records.
- Centralize Information: Define a single electronic repository for communication between departments.
2. Make Records Easy to Find
Across industries, more than half of office professionals report that they spend more time searching for information they already have but cannot locate efficiently than responding to client and in-house communications.

In effect, the speed at which records move from your various archives to the right screens and desks can make or break overall productivity.
In both cases, protecting your business from loss – internally to wasted time and externally to legal consequences – requires investment in two essential services.
- Quality document management software to speed up the conversion of paper to systematically indexed digital records
- Cloud-based digital storage to ensure those records are both protected and easily accessed
The Future of Records Management
At the end of 2021, 97% of decision-makers reported that adapting to conditions during the Covid-19 pandemic significantly accelerated their company’s digital transformation. Combined with a preexisting surge in global data creation, this trend has likely pushed the rate at which people create data far past our capacity to store it in any format.
At the same time, most businesses still have a long period of records management transition ahead of them. More than two-thirds continue to create paper records even while rushing to digitize those they already have.
This data migration won’t stop there either. As of April 2021, 33% of organizations reported having moved at least 50% of their workloads to the cloud. That percentage will rise to 56% by the end of 2022.
What does this mean for records management today?
For the time being, records management will remain a hybrid practice, charged with making sense of everything from hand-written notes on a legal pad to cloud analytics. The world of information management is in a period of transition, but most of it travels on a one-way street. Businesses can do themselves a future favor today by consistently keeping records of all formats organized according to the records lifecycle.
Try Document Management with FileCenter
FileCenter specializes in document management solutions that scale to the size and style of your existing business operations. FileCenter can help you achieve hassle-free document organization from corporate offices to private practices.
Start a free trial of FileCenter today.


